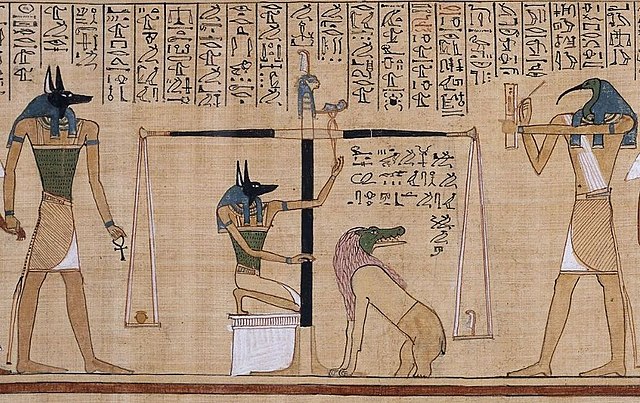
Amenta, also known as the “Amentet,” is a term from ancient Egyptian mythology and religion that holds fascinating historical and mystical significance. It represents the concept of the underworld or the afterlife and is closely associated with the journey of the deceased through the realm of the dead. Here’s a glimpse into the history and mysteries surrounding Amenta:
1. Meaning and Interpretation:
- Underworld and Afterlife: Amenta is often described as the Egyptian underworld, a realm that is both a physical place and a metaphysical concept. It is where the souls of the deceased would journey after death, and it played a central role in ancient Egyptian beliefs about the afterlife.
- West and the Setting Sun: Amenta is typically associated with the west, where the sun sets. In Egyptian cosmology, the west was seen as the direction of death and the afterlife, as opposed to the east, which was associated with life and rebirth.

2. Mythological Significance:
- Ra’s Nightly Journey: In Egyptian mythology, the sun god Ra was believed to travel through Amenta during his nightly journey through the underworld before rising again in the east. This journey symbolized the cyclical nature of the sun’s daily cycle and its passage through the realm of the dead.
- The Duat: Amenta is often equated with the Duat, another term for the Egyptian underworld. The Duat was envisioned as a series of realms or regions that the soul of the deceased would pass through, encountering various challenges and obstacles on the way to the afterlife.
3. Funerary Texts and Rituals:
- The Book of the Dead: Amenta and the Duat are prominently featured in ancient Egyptian funerary texts, particularly the Book of the Dead (also known as the Book of Coming Forth by Day). These texts contained spells, prayers, and instructions to guide the deceased safely through the afterlife and ensure a successful journey to the realm of the gods.
- Funerary Art and Architecture: Amenta and the Duat were also depicted in tomb paintings, reliefs, and architectural elements of tombs and temples. These artworks served as visual aids to assist the deceased in their journey and as a means of invoking divine protection.
4. Modern Interest:
- Amenta continues to be of interest to Egyptologists, archaeologists, and scholars of ancient Egyptian religion and mythology. The study of Amenta and related concepts sheds light on the complex beliefs and practices surrounding death and the afterlife in ancient Egypt.
In summary, Amenta is a captivating and essential concept in ancient Egyptian mythology and religion, representing the underworld and the journey of the soul through the afterlife. Its symbolism and significance are deeply intertwined with the cultural and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egypt, offering insights into their views on life, death, and the eternal cycle of existence.