Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotic microorganisms that play diverse roles in various ecosystems. While many protozoa are harmless, some species can impact human health, causing diseases. Here’s an exploration of protozoa, their impact on human health, and some notable diseases associated with them:
1. Parasitic Infections:
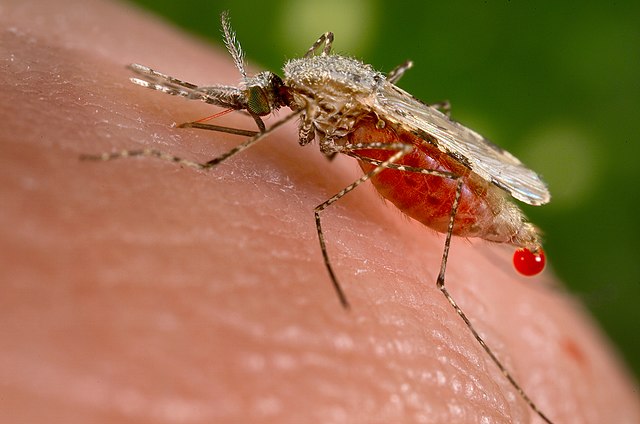
- Malaria (Plasmodium spp.): Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. These protozoa infect and multiply within red blood cells, leading to symptoms such as fever, chills, and anemia.

- Trypanosomiasis (Trypanosoma spp.): African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) and Chagas disease are caused by Trypanosoma parasites transmitted by tsetse flies and triatomine bugs, respectively. These infections can lead to severe neurological and cardiac complications.
- Leishmaniasis (Leishmania spp.): Leishmania parasites cause leishmaniasis, a disease transmitted through sandfly bites. The infection can manifest as cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral forms, affecting the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs.
2. Waterborne Diseases:
- Giardiasis (Giardia lamblia): Giardia lamblia is a protozoan parasite that causes giardiasis, a diarrheal illness. Contaminated water and food are common sources of transmission.
- Cryptosporidiosis (Cryptosporidium spp.): Cryptosporidium parasites can cause gastrointestinal illness. Contamination of water, food, and contact with infected individuals are common routes of transmission.
3. Toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii):
- Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that can be transmitted through the consumption of undercooked meat, contaminated water, or contact with infected cat feces. In healthy individuals, the infection is often asymptomatic, but it can cause severe complications in pregnant women and individuals with weakened immune systems.
4. Amoebic Infections:
- Amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica): Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebic dysentery and can lead to liver abscesses. Contaminated water and food are common sources of infection.
5. Algae and Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs):
- While not all algae are harmful, some produce toxins during blooms known as Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs). These toxins can contaminate water and seafood, leading to illnesses in humans.
6. Symbiotic Relationships:
- Some protozoa form symbiotic relationships with humans and are a part of the normal flora in the digestive system. Balancing these symbiotic relationships is important for maintaining a healthy microbiome.
7. Research and Treatment:
- Protozoa are essential in research, including studies on cell biology, genetics, and evolution. Understanding their life cycles and molecular processes is crucial for developing treatments for protozoan diseases.
Conclusion:
While some protozoa are integral to ecosystems and research, others can cause significant diseases in humans. Preventive measures such as proper hygiene, water sanitation, and control of insect vectors are essential to minimize the impact of protozoan diseases. Ongoing research aims to develop effective treatments and vaccines to combat these infections and mitigate their impact on human health.