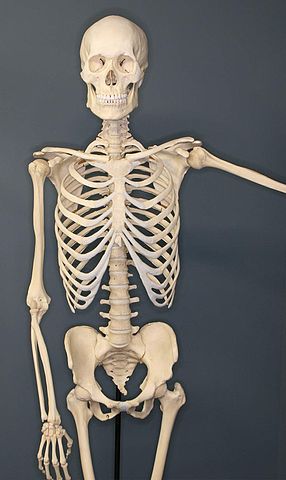
The skeletal system is a remarkable and essential component of the human body, providing structural support, protection, and facilitating various functions. Let’s unravel the mystery by exploring the structure and function of the skeletal system:
Structure of the Skeletal System:
- Bones: The human adult skeleton consists of 206 bones. These bones come in various shapes and sizes, with each serving specific functions in the body.
- Bone Tissue: Bones are composed of bone tissue, primarily made up of collagen and calcium phosphate. This combination provides strength and flexibility.
- Joints: Joints are the areas where two or more bones meet. They allow for movement and can be classified into different types, such as hinge, ball-and-socket, and pivot joints.
Functions of the Skeletal System:
- Support: The skeletal system provides the framework for the body, supporting and maintaining its shape.

- Protection: Many vital organs are protected by the skeletal system. For example, the skull shields the brain, the ribcage protects the heart and lungs, and the spine safeguards the spinal cord.
- Movement: The joints and muscles work in tandem with the skeletal system to facilitate movement. Muscles are anchored to bones, and when they contract, they pull on the bones, causing movement.
- Blood Cell Production: Within the cavities of certain bones (such as the ribs, sternum, and pelvis), a soft, spongy tissue called bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Mineral Storage: Bones serve as a reservoir for essential minerals, primarily calcium and phosphorus. When the body needs these minerals for various physiological functions, it can draw upon the skeletal stores.
- Endocrine Function: The skeletal system is involved in regulating the body’s calcium levels through the release of hormones. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin are two hormones that help maintain calcium balance.
- Leverage for Movement: Bones act as levers, and joints serve as pivot points. This lever system allows for a wide range of movements, from simple actions like walking to complex athletic activities.
- Hematopoiesis: Hematopoiesis is the production of blood cells within the bone marrow. It is essential for the body’s immune system and the transportation of oxygen and nutrients.
Types of Bones:
- Long Bones: These bones, such as the femur and humerus, are longer than they are wide and provide support as well as leverage for movement.
- Short Bones: Short bones, like those in the wrist (carpals) and ankle (tarsals), are roughly cube-shaped and provide stability and support.
- Flat Bones: Flat bones, including the skull, scapulae, and ribs, protect vital organs and offer surfaces for muscle attachment.
- Irregular Bones: Bones with complex shapes, like the vertebrae and certain facial bones, serve specific functions.
The skeletal system is a dynamic and adaptable part of the human body, constantly undergoing remodeling and renewal. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, mobility, and the protection of vital organs. Understanding the structure and function of the skeletal system is essential for appreciating the intricacies of human anatomy and physiology.