The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a fascinating and mysterious satellite galaxy that orbits our Milky Way. It is one of the closest galaxies to our own and provides a unique laboratory for studying various aspects of the universe. Here are some of the mysteries and marvels associated with the Large Magellanic Cloud:
1. Proximity:
The LMC is located at a distance of about 160,000 light-years from Earth, making it one of the nearest galaxies to us. Its proximity allows astronomers to study it in great detail.
2. Irregular Shape:
Unlike our Milky Way, which is a barred spiral galaxy, the LMC has an irregular shape with no well-defined spiral arms. Its irregularity raises questions about its formation and evolution.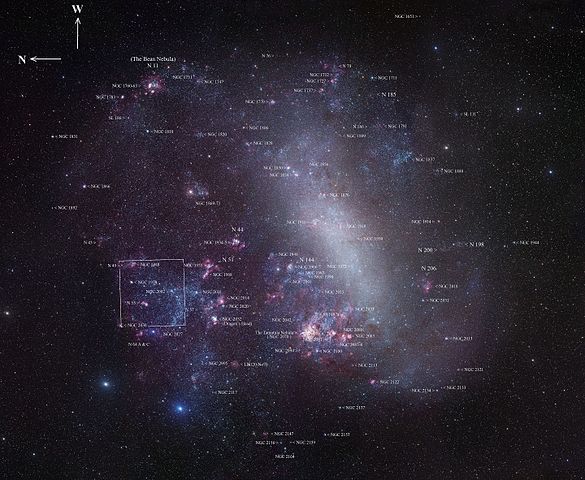
3. Interaction with the Milky Way:
The LMC is in a gravitational interaction with the Milky Way and is gradually being drawn closer to our galaxy. Understanding the dynamics of this interaction and its long-term consequences is a topic of ongoing research.
4. Star Formation:
The LMC is a hotbed of star formation. Its regions of active star formation, known as “HII regions,” are rich in young, massive stars and are critical for studying the processes of star birth and evolution.
5. Stellar Populations:
The LMC hosts a diverse population of stars, including stars of different ages, sizes, and compositions. The study of these stars helps astronomers piece together the galaxy’s history.
6. Supernovae:
The LMC has been the site of numerous supernovae explosions, which are powerful stellar explosions marking the end of a star’s life. These events have been closely observed and studied, contributing to our understanding of supernova mechanisms.
7. Cosmic Distance Indicator:
The LMC has been a vital tool for calibrating the cosmic distance ladder, allowing astronomers to determine distances to galaxies throughout the universe more accurately.
8. Dark Matter:
The LMC is believed to contain a significant amount of dark matter. Studying its gravitational effects can provide insights into the nature of this mysterious substance.
9. Magellanic Bridge and Stream:
The LMC is connected to its smaller companion, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), by a bridge of gas and stars. There is also a trailing stream of stars and gas that extends from the LMC, both of which are results of gravitational interactions.
10. Tidal Features:
The LMC exhibits prominent tidal features, including tidal tails and distortions, caused by the gravitational influence of the Milky Way. Understanding the formation and dynamics of these features is a complex challenge.
11. Dwarf Galaxies:
The LMC has its own population of dwarf galaxies, some of which are in the process of merging with it. These interactions are crucial for understanding galaxy evolution in the Local Group.
12. Ancient Observations:
The LMC has been known to astronomers since ancient times, with recorded observations dating back to Indigenous Australian cultures. It has played a significant role in human understanding of the cosmos.
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a celestial laboratory that offers a unique perspective on the processes of galaxy formation, evolution, and interaction. Unveiling its mysteries contributes not only to our knowledge of this particular galaxy but also to our broader understanding of the universe.











